Deforming osteoarthritis- a disease associated with degenerative changes (wear and tear) of the cartilage tissue that covers the articular surfaces of the bones and enables limb mobility.
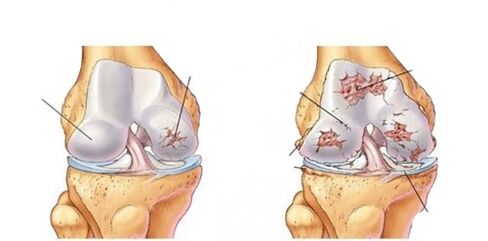
This is one of the most common musculoskeletal disorders (the incidence of the adult population in different regions of the world is between 13 and 29%). Deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis) is the second most common disease after deforming osteoarthritis of the hip joint.
Causes of osteoarthritis of the knee
The mechanism by which knee osteoarthritis develops is not yet fully understood. Nevertheless, the factors that contribute to the development of pathology have long been known. Some of them are inevitable - this is age, female gender, hereditary predisposition.
The reasons for the development of deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint, which leads to accelerated wear of the cartilage, are:
- Obesity (more than 66% of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee are overweight);
- pathologies of the musculoskeletal system that increase the load on the joint (scoliosis, osteochondrosis, flat feet, systemic diseases of the joints, etc. );
- increased physical activity, including exercise.
In addition, the progression of osteoarthritis of the knee is facilitated by pathologies that disrupt the metabolism of cartilage tissue (endocrine diseases, gout), as well as circulatory diseases (varicose veins of the lower extremities, arteriosclerosis of the leg arteries, diabetic angiopathy). Timely and adequate therapy for these diseases helps to maintain the function of the extremity for a long time.
Another common cause of osteoarthritis of the knee is a knee injury. In such cases, the pathology progresses unusually quickly. We therefore advise all patients who have suffered a knee injury to be examined in good time and, if necessary, undergo an arthroscopy of the knee joint to remove intra-articular injuries.
When should you see a traumatologist?
Immediately after the occurrence of the following symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee joint, an orthopedic traumatologist should be consulted:
- Knee pain is the most persistent symptom;
- Crunching when moving;
- morning stiffness - usually combined with some sort of "initial pain" and disappears after 30 minutes of exercise;
- Dysfunction of the joint - a feeling of looseness or, conversely, pathological stiffness, lameness, etc.
Experienced orthopedic traumatologists are appointed to the MC who, after a detailed diagnosis, select the optimal treatment method for the knee joint: surgery or conservative therapy, depending on the situation.